

And here’s a fun little nugget for you – as wonderful as this ability would be, absolute recall for the duration of a lifetime has never actually been proven to exist.
#EIDETIC MEMORY EXAMPLES SERIES#
It’s what the character Michael Ross in the TV legal series “Suits” possesses. Photographic memory is defined as the ability to recall information like text, numbers, or similar, for a long period of time after only briefly looking at the material, and without the intense visualization part. So now on to a quick explainer of photographic memory. And that, friends, is why what you think is eidetic is likely not the case at all. Furthermore, you’d also be able to do this without using other mnemonic devices.
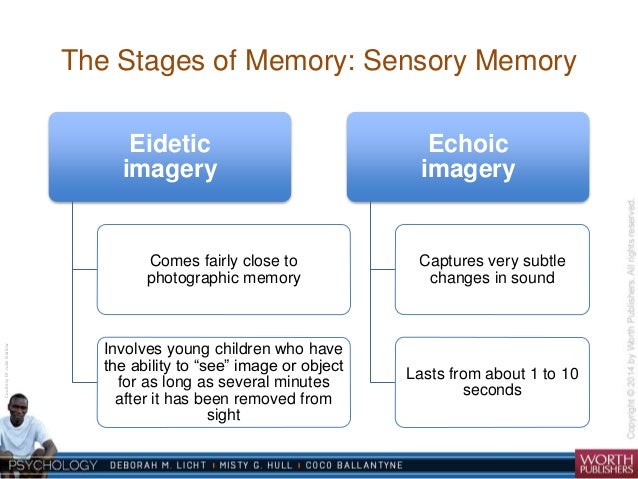
This is most likely down to language acquisition and the brain switching from visual memory systems to abstract systems, which leads to a suppression of visual memory systems.Īnd here’s the main caveat: According to the author of Memory and Learning, Andrew Hudmon, a person with eidetic memory would “remember an image in so much detail, clarity, and accuracy that it is as though the image were still being perceived”. True eidetic memory is incredibly rare and more likely to be found in children rather than adults. Wow, you can do that already, so are you an eidetiker? What’s the difference between eidetic memory and photographic memory? These people are sometimes referred to as eidetikers. For example, you’d be able to look at an image or a photograph only once and clearly be able to recall its details for a short while. And when we say short, we mean in the region of 30 seconds. Eidetic memory is the ability to clearly see an image in your mind’s eye for a short period of time after seeing it. While they’re similar, they’re not actually the same.Įidetic comes from the Greek word “edios”, which means “visible form”. Eidetic memory is often used interchangeably with photographic memory. The first mistake people often make starts with the definition. Let’s start with an eidetic memory definition What’s the difference between eidetic memory and photographic memory?.Let’s start with an eidetic memory definition.An Eidetiker will be able to repeat three or four times as many as the average individual. Here the test is to read aloud a long list of digits and ask the subject to repeat them. Occasionally one comes across an acoustic,or auditory, Eidetiker. A true Eidetiker will summon up the image and count the teeth even after several minutes or even hours have elapsed. An even simpler test is to show him a comb for a moment, then ask him how many teeth it contained. If he is a genuine Eidetiker, he will be able to describe every detail and repeat the number or the letters of the word forward and backward. A similar if not identical phenomenon is occasionally found in patients with tetany and Basedow’s disease (hyperthyroidism).A common test for eidetic imagery is to ask a subject to look briefly at a picture containing many details, including, say, a twelve-digit figure, or a long word in a language he does not know. The images are so vivid and realistic that they are sometimes momentarily mistaken for the actual objects. In addition, adults occasionally experience a form of eidetic imagery for a short time after engaging in fatiguing activity of a monotonous nature, such as playing cards or closely studying blueprints. Some “lightning calculators” are Eidetikers who are able to keep one part of a long problem on their “mental blackboard” while working on another. The few adults who retain this ability can often perform feats of “photographic memory,” such as repeating the entire content of a newspaper page after looking at it for only a few minutes.

Some “Eidetikers” claim they can even enlarge portions of the mental picture in order to see them more clearly.Eidetic imagery is found in 5 to 10 per cent of children, but usually disappears before adolescence. They appear to “project” the image on a mental screen and are able to describe every detail as if they were still looking at the object itself. Mental imagery, usually visual, which closely resembles actual perception.Some people are able to look at a drawing or page of print for a short time and later see it in their “mind’s eye” with amazing vividness.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
